Introduction
Elementor supports a wider range of measurement units giving you immense design flexibility. For more details about some of the commonly used units, check out our article – What’s The Difference Between PX, EM, REM, %, VW, and VH?
Choosing a unit
Any option requiring a measurement unit, includes a unit it is measured by (e.g. PX for pixels).

Click this unit of measurement to open a menu letting you to switch measurement units.
Custom measurements
Some web creators prefer to use CSS math functions to set measurements.
Example: The headline on Alex’s site is set to 4 EM. Drew prefers to use CSS math functions and so sets the font size to: calc(2.5EM + 2vw). This means the header on Drew’s site will be 2.5 EM plus 2% of the viewport width (the width of the browser screen). By using a math function dependent on viewport width, Drew’s design will be fine-tuned to any screen size.
CSS math functions can make your site more accurate, more responsive and allows you to combine units of measurement (e.g. pixels and VH)
Elementor supports use of custom CSS math functions for a number of elements – containers, sections, columns, as well as typography controls.
How to add custom measurements
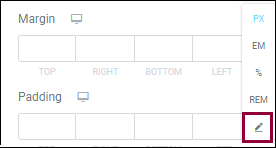
- Open the unit selection dropdown as described above.
- Select the pencil icon.
- Enter the CSS math function in the text box (e.g. calc(2.5em + 2vw))
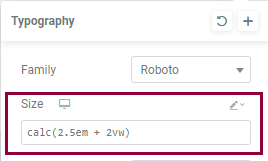
When entering CSS math functions, please keep in mind:
- You must include the unit of measurement (e.g. 50PX not 50)
- Make sure there are no spaces between value and the unit (50PX not 50 PX)