Many Search Engine Optimization (SEO) experts focus on driving traffic to your blog or business website. However, SEO is also important for ecommerce stores. If you’re lagging behind in Google’s search results, then you could also be missing out on sales.
In this article, we’ll explore why SEO is crucial for ecommerce success. We’ll then share 13 tips for improving your store’s SEO, including how to create search engine-friendly templates for your products and product categories. Let’s get to work!
Table of Contents
- What Is Ecommerce SEO?
- Why Is SEO Important for Your Ecommerce Site?
- How Does Ecommerce SEO Work?
- A Step-by-Step Guide To Ecommerce SEO (13 Key Steps)
- Step 1: Conduct Keyword Research
- Step 2: Research Your Competitors
- Step 3: Optimize Your Product Pages
- Step 4: Optimize Your Snippets
- Step 5: Optimize Your Category and Tag Archives
- Step 6: Consider Modifying Your Breadcrumbs
- Step 7: Test Your robots.txt File
- Step 8: Switch To HTTPS
- Step 9: Test Your Store’s Performance
- Step 10: Consider Using a Third-Party SEO Plugin
- Step 11: Create an SEO Content Marketing Strategy
- Step 12: Secure Valuable Backlinks
- Step 13: Don’t Forget About Internal Links
- How To Optimize the Organic Traffic Conversion Rate
- How To Analyze Your Ecommerce SEO Strategy’s Success
What Is Ecommerce SEO?
Ecommerce SEO is the process of improving your online store’s visibility in search engine results pages and generating more organic (free) traffic to your ecommerce website. The Ecommerce SEO process typically involves on-page optimization, technical improvements, and fine-tuning your website’s structure.
There are multiple acquisition channels for ecommerce sites, but SEO is crucial to long-term success. Fortunately, there are plenty of techniques that can help your store climb the search engine rankings. By performing thorough, product-focused keyword research and learning from your competitors, you can get your ecommerce SEO strategy off to the best possible start.
A little confused?
Think of it this way:
“SEO is just like external signage on a physical store. Without it, how are customers to know what you sell, let alone where to find you?”
– A2X
Why Is SEO Important for Your Ecommerce Site?
Regardless of your business’ size, target audience, or industry, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is essential for maximizing your profits. Search engines such as Google are now an integral part of the online shopping experience.
You can verify this using any analytics platform, including Google Analytics. Simply log in to your chosen platform, and examine your main sources of traffic. Chances are that organic search will feature prominently. In fact, for many ecommerce stores, Google is their number-one source of traffic.
When you look at the numbers, it’s easy to see why. According to the Global Digital Overview, Google.com is the most visited website in the world. This places it above many other household names, including YouTube, Facebook, Amazon, and Netflix.
It’s estimated that 40–60 billion searches happen on Google in the US every single month. For ecommerce stores, organic search means a huge potential audience, and lots of additional revenue just waiting to be tapped into. In fact, over 40 percent of revenue for most stores can be attributed to organic traffic, and 39 percent of online purchases are influenced by a relevant search.
Organic search results are also far more attractive to users when compared to more traditional, paid advertising. According to research, 62.2 percent of Google searches performed on desktop devices result in an organic click, while only 2.8 percent result in a paid click.
These figures are similar on mobile devices, where about 41 percent of mobile searches result in an organic click. This is a dramatic increase over paid advertising, where only 2 percent of searches result in a paid click. By concentrating on SEO, you can expect 20 times more traffic opportunities than Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising offers on both desktop and mobile.
In other words, it’s impossible to deny how important SEO is to your online store’s success. If you neglect SEO, you’re limiting your business’ growth and profits.
How Does Ecommerce SEO Work?
Search engines use a combination of crawlers (bots), indexes, and algorithms to determine which content deserves the top spot. To give your store the best chance of ranking high, it’s worth exploring the science behind how search engines work.
The process starts with “crawling”. This is where search engines send out a team of bots that find new and updated content. That might include a product you’ve just added to your store or a new review left by a satisfied customer.
The discovered content is then stored in a database known as an index. Once your content is in Google’s index, it’s in the running to appear in relevant search results. Whenever someone performs a search, Google will scour its index for relevant content. If yours is deemed a good match for the query, then it’s more likely to be included in the search results.
Google arranges its content in a way that’s designed to resolve the search query as efficiently as possible. This process is known as ranking. Your page’s rankings will determine where they appear in the search results. The higher each page ranks, the closer it will appear to the coveted number-one spot.
Where your store appears in search results can have a huge impact on how much traffic it receives. Moving up just one spot in Google’s results can increase your Click Through Rates (CTRs) by more than 53 percent. This could translate to a significant increase in visits, conversions, and ultimately more revenue for your ecommerce store.
What’s more, the first page of Google receives 95 percent of web traffic, with subsequent pages receiving five percent or less of total traffic. If you excel at SEO and manage to score that lucrative number-one spot, then your store is 10 times more likely to receive a click as compared to a page in the tenth spot. That’s an advantage well worth pursuing.
A Step-by-Step Guide To Ecommerce SEO (13 Key Steps)
As we’ve seen, SEO is critical for driving traffic, boosting leads, and generating sales. If your ecommerce site is going to thrive, then it’s essential that you climb the search engine results, and get the virtual foot traffic your store deserves.
With that in mind, let’s look at 13 ways you can perform ecommerce SEO.
Step 1: Conduct Keyword Research
Keyword research is where you identify words and phrases that people use when searching for content that’s relevant to your ecommerce store. This includes your services and products.
Keyword research is essential for any successful SEO strategy. The phrases you identify during this step will inform all of your subsequent optimization efforts.
There are two basic categories of keywords:
- Informational: These are terms that people use to discover informative content, such as how-tos and tutorials. If your ecommerce store has a blog, then these are the terms you’ll be looking to target.
- Product/Transactional: These are terms used by people looking for a certain product. For an ecommerce website, these terms will form the core of your keyword strategy.
Finding the Right Keywords
To find the right keywords to target, you’ll need to research the most popular search terms used by people looking for your products.
You can find keywords by using Google automated suggestions and ‘people also ask’ features. These provide useful indications of the most popular keywords. You can also take a look at your successful competitors to see which terminology they’re using for their SEO strategy and emulate them
For ecommerce searches, Amazon is just as popular as Google. You can learn from the best by examining Amazon’s keyword strategies. Head over to Amazon and enter keywords that describe your products. Amazon will then make suggestions based on each phrase:
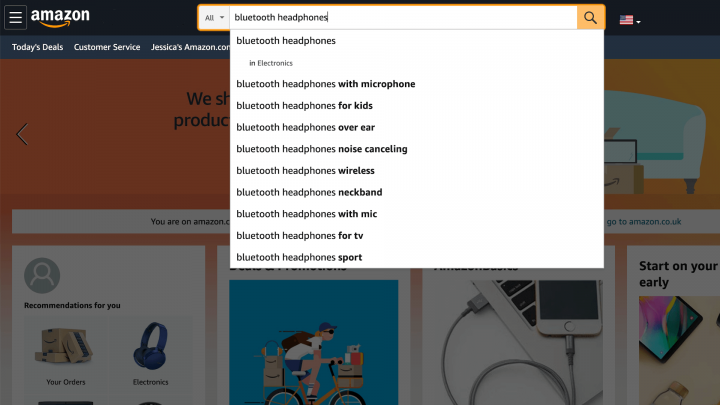
These suggestions are a great starting point for your SEO strategy, as they’re terms your customers are likely to be using. You’ll also notice that these suggestions tend to be long-tail keywords, which can be less competitive.
Alternatively, you can explore Amazon’s search suggestions using a standalone solution such as Keyword Tool Dominator.
Keyword Research Tools
Amazon is a great place to start, but it isn’t the only place where you can perform keyword research. There are a lot of top-quality solutions out there that can help you out. Some excellent tools to get started with include KWFinder, Ahrefs, and Keyword Explorer.
The SEMrush visibility management platform also provides keyword research solutions. You can perform a quick analysis using Keyword Overview, while Keyword Magic is perfect for identifying long-tail keywords:
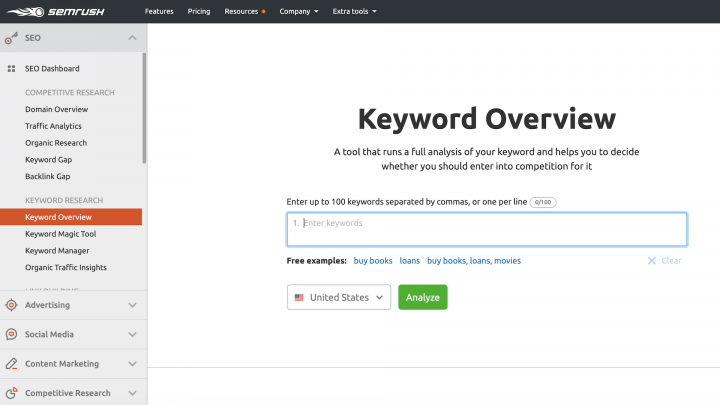
You can then use Ads History to identify whether these keywords were previously used in paid searches. If a keyword was featured in an ad, then you can view the amount of traffic generated from that promotion. This can help you gauge the amount of interest in the keywords you’re considering targeting.
Finally, you can use Keyword Difficulty to estimate how challenging it would be to outrank the pages that are currently presented for each keyword. When determining which keywords to target, you should focus on “untapped keywords” wherever possible. These are keywords that have a decent search volume and low competition and have the potential to deliver the highest Return On Investment (ROI).
Exactly what a good search volume is can vary depending on your industry. However, be wary of keywords that get a very low amount of searches. If no one is using a particular phrase, then it doesn’t matter how well that term converts.
Step 2: Research Your Competitors
The world of ecommerce is highly competitive. However, this can be a good thing, as you can learn from similar businesses. Competitor research involves analyzing your competitors’ SEO strategies. You can then identify the tactics that are working, and reverse-engineer them to use for your own store.
There are several ways to perform competitor research, but one of the most effective is keyword analysis, also known as keyword gap analysis. This is where you use a tool such as Moz’s Keyword Explorer to identify the terms that your competitors are ranking highly for:
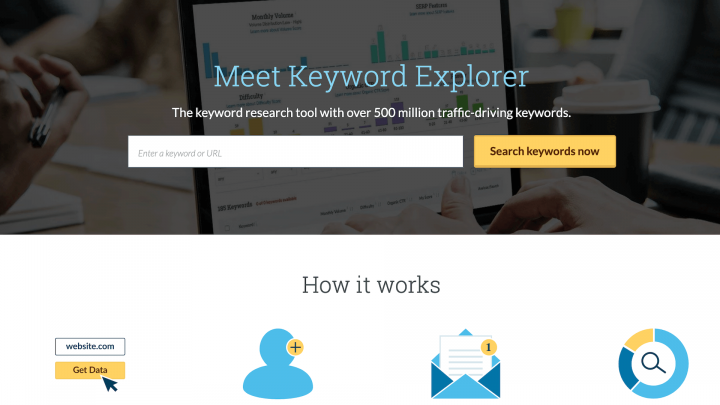
Then you can analyze those high-performing keywords and identify any that are relevant to your business. For best results, you can focus on keywords where your competitors are outperforming you by a significant margin.
If you manage to improve your rankings for these relevant, high-performing keywords, then you could experience a significant SEO boost. This can improve your traffic and conversions. It also improves your chances of outperforming your competitors and becoming a market leader in your field.
Another technique is to identify competitor content that has generated a lot of backlinks. Links from third-party websites can significantly improve your search engine rankings. You can identify your competitor’s most popular and frequently-linked content using a tool such as Link Explorer.
Simply enter your competitor’s domain, and open the Top Pages tab. This report will display all of the domain’s linked URLs. Then you can input these top-performing URLs into a keyword research tool, such as Moz’s Ranking Keywords, to see which ones attracted the most external links. This is useful information for informing your own SEO and content creation strategies.
Step 3: Optimize Your Product Pages
Once you’ve performed your keyword and competitor research, you can start to use this information to optimize your on-page SEO. This is where you improve your homepage and inner pages to help them rank higher in search engines such as Google.
Product Descriptions
Chances are that your ecommerce site features a large number of product pages. The typical product page contains many elements, but the description tends to be the most text-heavy element. This means it offers the most opportunities to optimize on-page SEO.
If you’re using the popular WooCommerece ecommerce platform, then you can define two separate product descriptions:
- A short description. Most WooCommerce themes display this description immediately after the product title, and alongside its images.
- A long description. This usually appears beneath the short description.
While these texts should provide relevant information to shoppers, they’re also a great place to include keywords. Wherever possible, try to use your target keywords at least once in both your short description and long description (but make sure to incorporate them organically).
H1-Tags
When it comes to headings, it’s important to ensure that each product page features a single primary title, marked with an H1 tag. Search engine bots will use heading tags to identify your product page’s most important content. Placing multiple H1s on the same page can confuse these bots, and negatively impact your SEO.
Images
Most product pages will also feature at least one image. For an extra SEO boost, it’s important to optimize the alt text and file names associated with each image.
Alt text can provide Google with valuable information about an image’s content. This increases your chances of ranking product images in Google Image Searches. You can set your image alt text by editing the image and using the Alt Text box:
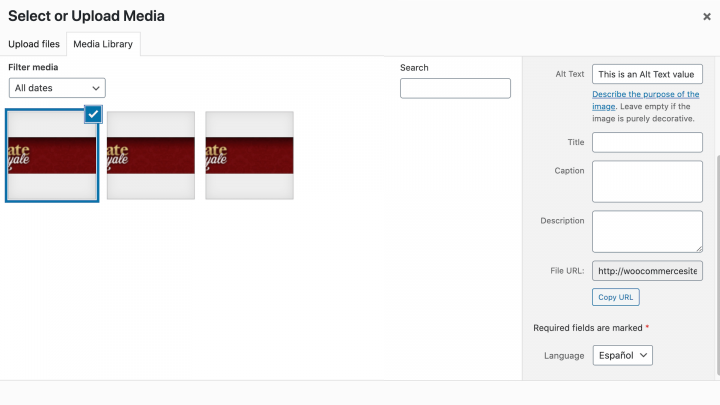
It’s also a good idea to use relevant keywords for your image file names. For example, instead of “product-inventory-1423.jpg”, you could label an image “red-laptop-case.jpg”.
Step 4: Optimize Your Snippets
The snippet is the text that represents your web page in Google’s search results. To optimize a page’s snippet, we recommend using a dedicated SEO plugin to optimize the following:
Meta Title
The meta title, also known as the title tag, is a key indicator to Google about the page’s content. The perfect title is informative and attention-grabbing, encouraging people to click on your link in the search results. The meta title doesn’t necessarily have to be the same as the product or page title.
Meta Description
The meta description should be short, succinct, and compelling. There’s no need to include keywords here, but the few sentences used for the description should be relevant to the search. To encourage people to click on your search results, you may want to highlight incentives such as low prices or free shipping.
URL Slug
This is another way to feed search engines important contextual information about a page’s contents. For ecommerce sites, the auto-generated URL slugs can be complex, particularly when products are nested in multiple sub-categories. It’s a good idea to shorten your URLs, to make them as concise as possible.
Structured Data
It’s also a good idea to explore the worlds of rich snippets. These snippets are used to present richer search results on a Google results page. They can appear as reviews, star ratings, opening times, recipes, events, etc.
Rich snippets use schema markup – HTML code which site operations can add to the page’s existing code. If you’re already using Elementor, you can use the star rating widget, which comes with pre-built rich snippets and Google structured mark-up capabilities.
Rich snippets are not a direct SEO ranking factor. However, they can help your ecommerce site stand out in Google’s search results, which can boost your CTRs. If you’re using WooCommerce, this widget will automatically add some structured data for products.
Step 5: Optimize Your Category and Tag Archives
Optimizing your single product pages is a great start. However, it’s also a good idea to take a close look at your category pages and tags. Creating unique SEO descriptions for both your category and tag pages helps Google to understand what each page is all about, so it can rank that page appropriately.
You can write a unique SEO title and description for each category or tag using a plugin such as Yoast SEO. In the WordPress dashboard, navigate to either Products > Categories, or Products > Tags:
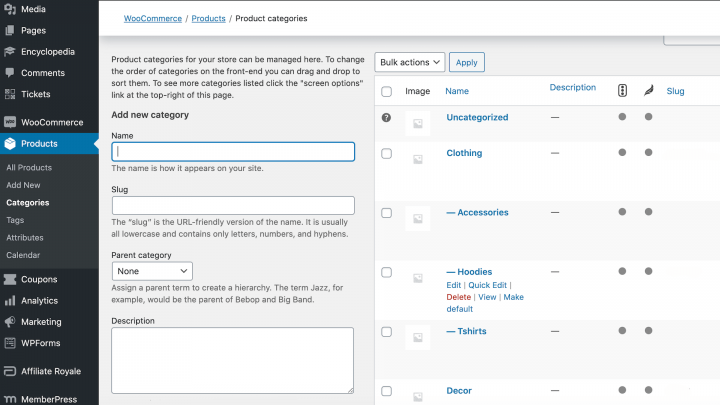
You can then open the tag or category for editing. Next, scroll down to the Yoast SEO box and create your descriptions. To make these as SEO-friendly as possible, we recommend including relevant keywords, including long-tail variations.
Some themes will automatically display the description that you set in a category or tag’s settings. However, not all themes display this information. In that case, you can add these descriptions using Elementor WooCommerce Builder. For example, to display the category description you can add Elementor’s Archive Description to your product category template.
Step 6: Consider Modifying Your Breadcrumbs
A breadcrumb or breadcrumb trail is a line of text, often located at the top of a page. This indicates the user’s location within your store:
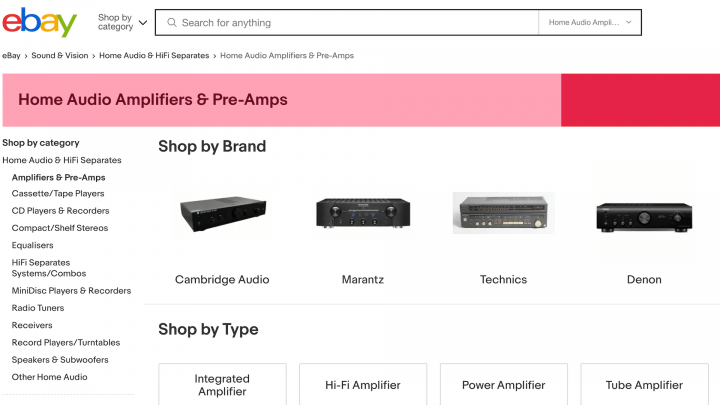
Many different kinds of websites use breadcrumbs as a navigational aid. However, they are particularly useful for ecommerce stores, where products are often nested inside a hierarchy of categories and sub-categories.
As a navigational tool, breadcrumbs help improve the User Experience (UX). When customers are enjoying their time in your store, they’re more likely to continue browsing. This increases key SEO metrics, such as session duration and number of pages visited. It can also directly translate into sales, as the more products a customer views, the more likely they are to make a purchase.
Breadcrumbs help Google understand and crawl your ecommerce store, which can improve your rankings. Google will also display breadcrumbs in its search results. This can help potential customers understand the contents of your web page before clicking on it.
WooCommerce comes with its own breadcrumbs feature. However, you can get more control over your breadcrumbs by using PHP filters. You can also manually adjust WooCommerce’s native breadcrumbs using an SEO plugin.
For example, Yoast SEO can customize the contents of each product’s auto-generated breadcrumbs. To do this, navigate to Yoast SEO > Search Appearance > Breadcrumbs:
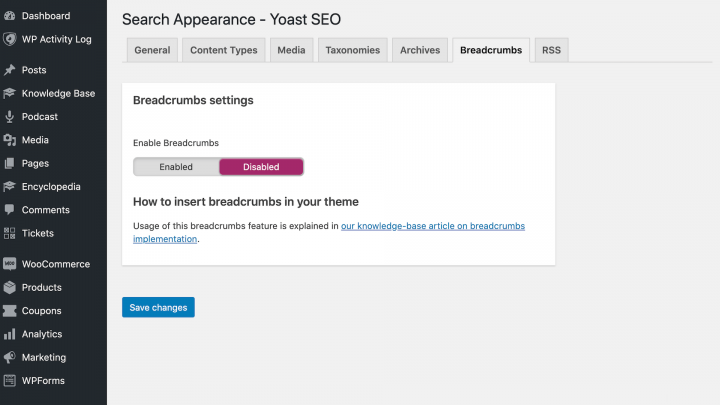
Yoast SEO also adds JSON-LD structured data. This increases the chances that Google will feature your breadcrumbs in its search results.
If you’re using Elementor WooCommerce Builder, you’ll also get a dedicated WooCommerce Breadcrumbs widget. This enables you to display breadcrumbs anywhere on your ecommerce store.
Step 7: Test Your robots.txt File
Your website’s robots.txt file provides instructions to the crawlers that are responsible for searching the web and recording information about its content. You can use this file to specify which parts of your site these crawlers can access, and which parts they should ignore.
If your robots.txt file is configured incorrectly, then it can prevent Google from crawling and indexing specific product pages, or even your entire ecommerce store. Even simple formatting errors can prevent some of your pages from being indexed correctly, having a disastrous impact on your SEO.
To make sure search engines can actually see all of your products, you should ensure that your robots.txt file is configured correctly. You can test this using Google’s robots.txt Tester tool.

If this tool identifies an issue with your robots.txt file, then you can edit it using an SEO plugin. If you’re using Yoast SEO, you can navigate to SEO > Tools and select File Editor:
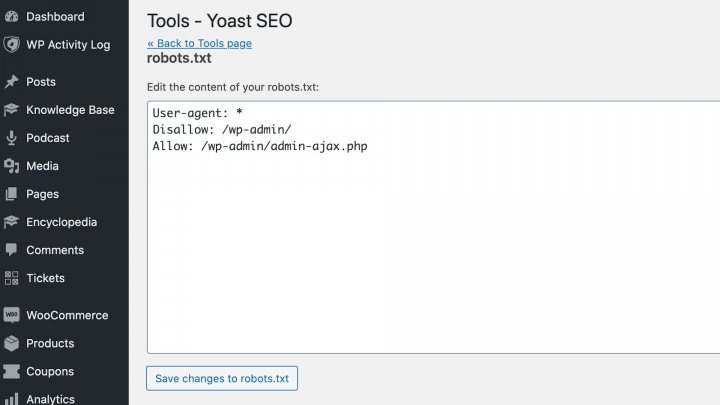
Yoast SEO will display your robots.txt file, and you can edit it or upload an alternative file as needed.
Step 8: Switch to HTTPS
Since you’ll likely be handling payments through your ecommerce site, it’s crucial to provide a secure connection using Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). HTTPS is a protocol that encrypts the data sent between your web server and the customer’s browser.
Switching to HTTPS can help keep your customers safe. It can also improve your SEO, as Google uses HTTPS as a ranking signal: “For now it’s only a very lightweight signal….But over time, we may decide to strengthen it, because we’d like to encourage all website owners to switch from HTTP to HTTPS to keep everyone safe on the web.”
After analyzing one million Google search results, SEO specialist and founder of Backlinko Brian Dean confirmed that switching to HTTPS does have a positive impact on search engine rankings. The 2019 Ranking Factors Study conducted by SEMrush also concluded that HTTPS is now a very strong ranking factor.
Therefore, it’s a good idea to verify that your ecommerce store is using HTTPS. If it isn’t, we’d highly recommend making the switch, as it will almost certainly have a positive impact on your store’s search engine rankings (and keep your customers’ transactions safe).
Step 9: Test Your Store’s Performance
It’s also a good idea to explore the worlds of rich snippets. These snippets are used to present richer search results on a Google results page. They can appear as reviews, star ratings, opening times, recipes, events, etc.
Rich snippets use schema markup – HTML code which site operations can add to the page’s existing code. If you’re already using Elementor, you can use the star rating widget, which comes with pre-built rich snippets and Google structured mark-up capabilities.
Rich snippets are not a direct SEO ranking factor. However, they can help your ecommerce site stand out in Google’s search results, which can boost your CTRs. If you’re using WooCommerce, this widget will automatically add some structured data for products.
To keep your WooCommerce site running fast, you can follow the tips in our guide to speeding up WordPress. You can also improve performance using the WP Rocket plugin, which even has built-in integration for WooCommerce.
When it comes to testing your website’s performance, we’d recommend the following tools:
- Google PageSpeed Insights. This platform evaluates how well your store performs on both desktop and mobile devices. It will then offer suggestions and best practices for boosting your website’s speed and overall performance.
- Pingdom by SolarWinds. You can use this platform to test your website, but Pingdom also provides automated uptime monitoring. A recent study by Moz found that intermittent 500 internal server errors can cause issues with tracked keywords. If your store is offline for a significant amount of time, that could have a negative impact on SEO. Pingdom can notify you if your ecommerce store experiences any downtime. This helps you resolve the issue before it has a chance to impact your SEO.
- GTmetrix. This platform provides detailed, real-time performance tracking. The in-depth metrics include a visual representation of how every single asset on your website loads, including your CSS, HTML, JavaScript, images, plugins, and third-party content. GTmetrix also provides recommendations for improving your store’s performance.
It’s a smart idea to test your store on a regular basis. This helps you identify and resolve any issues promptly before they degrade your SEO. It also means you can continuously refine your store’s performance — and by extension its rankings.
Step 10: Consider Using a Third-Party SEO Plugin

As we’ve mentioned, Yoast SEO is a great option for WooCommerce stores. Even better, there’s a dedicated Yoast WooCommerce SEO extension. This extension adds some useful features specifically designed for online stores, including rich ecommerce details for specific social media platforms. This can be useful if your products receive a lot of shares on social sites.
The WooCommerce extension also cleans up your XML sitemap. This removes irrelevant content, which is useful since the WooCommerce platform does have a reputation for creating a lot of duplicate content.
For example, all the parameters that your customers use to filter your products will create extra URLs that feature duplicate content. You don’t want Google focusing its resources on indexing these pages when it could be concentrating on the content that you actually want it to rank.
Another popular SEO plugin is Rank Math. This tool has built-in compatibility with Elementor, which is great if you’re planning to use Elementor WooCommerce Builder to design your store.
Alternatively, you can use the All in One SEO Pack. The free version of this plugin comes with basic support for WooCommerce. However, you’ll need to purchase the Pro version to unlock additional WooCommerce-related features, including setting SEO titles and meta descriptions for product category and tag archives.
Step 11: Create an SEO Content Marketing Strategy
Content marketing is the process of creating various forms of content, including blog posts, videos, and infographics. This content can attract more traffic to your store, and ultimately drive conversions.
The key to a successful content marketing strategy is to provide your readers with valuable information, especially if it helps them resolve a pertinent problem. This creates a sense of trust that first-time buyers may need before sharing their credit card details with an online store.
By publishing useful content on a regular basis, you can build a long-term relationship with your customers. You can also inspire a sense of brand loyalty that can transform one-time purchasers into loyal repeat customers.
For the best results, it’s a good idea to identify the challenges your customers are currently experiencing. You can then produce content that helps them overcome those problems. It may help to interview your target audience about the issues they’re facing, and the topics they’re interested in. You can then create a content calendar that’s tailored to meet their exact needs.
Your previous research can also come in useful. Ideally, you should have a list of high-value keywords that are relevant to your ecommerce store. You can build some of your content around those terms.
You can also use your competitor research to influence your content marketing strategy. For example, if a competitor’s post gained an unusually large number of backlinks, then you might create content that covers a similar topic. You can then reach out to the third parties that linked to the existing content, to see whether they’re interested in featuring yours instead.
Finally, when it’s time to publish your content, try to include at least one relevant Call To Action (CTA). This is essential for converting traffic into paying customers.
Step 12: Secure Valuable Backlinks
Link building plays a vital role in SEO. When an external website links to your ecommerce store, search engines count that as an endorsement of your store’s content. Each external link will pass authority, relevancy, and trust to your site. You can measure the strength of your backlink profile by checking the Domain Authority and Page Authority in a tool such as Ahrefs – just be aware that these are private metrics that are not used by Google so they should only be used as an initial reference point.
The most valuable external links come from sources that are trusted by Google. This might include established websites that have a large following, and a long history of obeying Google’s guidelines. The source should also be topically related to your website’s content. For example, if your electronics store receives a link from a blog discussing the best smart TVs of 2020, then this is great for your SEO.
The best way to earn backlinks is to produce valuable content. This might involve creating long and in-depth posts, or concentrating on content forms that are proven to attract plenty of external links. According to a study by BuzzSumo, 75 percent of all online content gets zero links, while some types of content are greatly preferred. Popular options for backlinks include list posts, quizzes, videos, infographics, and how-to articles.
It may also help to perform a link gap analysis. This is where you identify links your competitors have earned that are relevant to your ecommerce site. You can use Link Explorer’s Link Intersect tool to identify domains and URLs that link to your competitors, but not to you. This gives you a list of places to target as a part of your external link-building strategy.
Step 13: Don’t Forget About Internal Links
SEO experts put a lot of emphasis on external links, but internal links can also boost your SEO. While backlinks are hyperlinks between two different websites, an internal link is a hyperlink between two different pages of the same website.
Although they’re often overlooked, internal links can have a positive impact on SEO. Research suggests that session duration and the number of pages visited per session are two of the most important ranking factors. Internal links can boost both of these metrics by helping visitors find related content.
Additionally, internal links help to define your site architecture – i.e. the relationship between the pages on your site, and where they fit within the website’s overall structure. Inner pages with lots of internal links will be seen as more valuable. Likewise, pages with internal links from high-value pages, such as the homepage, are seen as focal to your website.
The great thing about internal links is that you’re in control. This means you can choose your own anchor text. Ideally, the anchor text should contain keywords that you want the page to rank for.
Anchor text can also be branded or unbranded. Branded links contain your store’s name, and are useful for improving visibility. For internal links, we recommend using non-branded anchor text, unless the page you’re linking to only has branded content and doesn’t rank for non-branded terms.
Fortunately, it’s easy to create an internal link in Elementor. Simply select the text that you want to link in the text editor, and it will automatically suggest relevant content you can link to.
After adding your internal links, it’s a good idea to monitor the health of those URLs. A study of over 450 million web pages found that 80 percent of the websites had broken links. This can have a negative impact on the customer experience, and damage your SEO.
You can use a backlink health checking tool, such as Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider, to identify unhealthy link behavior, including broken links. After finding a problematic URL, you can either update it, set up a redirect, or remove it entirely.
How To Optimize the Organic Traffic Conversion Rate
Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO) involves trying to increase the percentage of visitors who convert on your website. For ecommerce stores, this typically involves transforming visitors into paying customers.
Just as with a physical storefront, it’s important to get a large number of people through the door. However, if most of those people are content to browse without ever making a purchase, your business will struggle to turn a profit. By concentrating on CRO, on the other hand, you can get more customers from the same amount of traffic.
A successful CRO strategy involves making the purchasing process frictionless. It’s a smart idea to use tracking tools to map the journey buyers take through your ecommerce store. You can then focus your efforts on refining that path. This often involves providing a clear sales funnel, from the moment the visitor arrives on your website right through to the point when they complete the checkout process.
To provide a better purchasing experience, you can also offer multiple payment gateways. This lets customers choose how they want to pay. Wherever possible, it’s also a good idea to give customers the option to check out without creating an account.
To deliver a seamless customer experience, it may help to conduct customer surveys or perform A/B testing and experiment with various CTAs. For example, a recent test by HubSpot found that anchor text CTAs delivered a much higher conversion rate than end-of-post banners. Every website is unique, so rather than guess what your customers will respond positively to, it’s always a good idea to put your theories to the test.
How To Analyze Your Ecommerce SEO Strategy’s Success
SEO optimization isn’t a one time task. Search engines such as Google are notorious for changing their algorithms and ranking factors over time. If you want to maintain your search position, then be prepared to monitor your website’s performance and refine your SEO accordingly.
You may also add content to your ecommerce store. This might include new products or blog posts that you generate as a part of your content marketing strategy. To help Google understand and rank this new content, it’s a smart move to perform SEO optimization on every piece of new content that you publish.
You can also monitor your SEO using tools such as Google Analytics. In particular, we’d recommend paying careful attention to traffic numbers, and time spent in your store. You can use these metrics to identify and improve issues. For example, a high volume of traffic but a low percentage of repeat visitors may indicate that your store is struggling to hold customer interest.
Boosting Your Sales With Ecommerce SEO
If your products aren’t ranking highly in Google’s search results, then you could be missing out on sales. Thankfully, by following our ecommerce SEO tips, you can climb the rankings and maybe even score that coveted number-one spot.
By conducting thorough keyword research and learning from your competitors, you can get your SEO strategy off to a strong start. You can then optimize your product pages to help them rank higher in search engines, using techniques such as snippets and breadcrumbs. Finally, you can increase key metrics, including session duration and number of pages visited, with an effective content marketing strategy.
Do you have any questions about using SEO to drive traffic to your ecommerce store? Ask away in the comments below!
Looking for fresh content?
By entering your email, you agree to receive Elementor emails, including marketing emails,
and agree to our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy.


